Syngas is used to generate electricity with high efficiency and lower emissions.
- Need Assistance? We're Here to Help! Contact Us:
- phone (215) 335-3180 | (202) 844-0990
- emailinfo@tansatech.com
- access_time Mon - Fri: 8am - 6pm
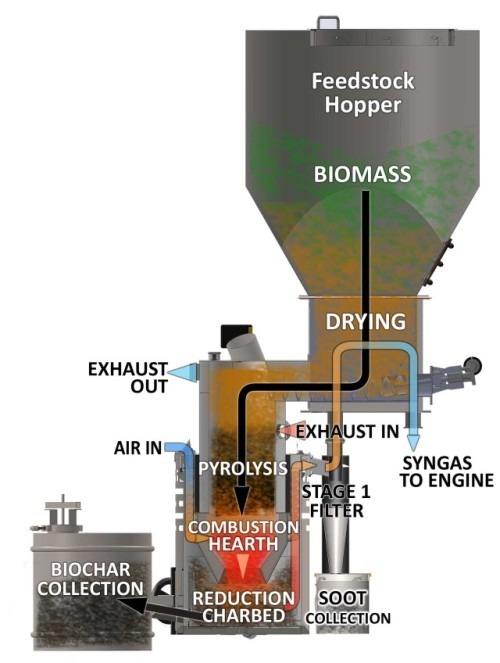
What is Gasification?
Gasification is a thermochemical process that converts carbon-containing feedstocks—such as coal, biomass, or waste—into a mixture of gases known as syngas. This process occurs in a high-temperature, controlled environment with limited oxygen or steam, facilitating partial oxidation. The resultant syngas, primarily composed of hydrogen (H₂) and carbon monoxide (CO), can be further refined and utilized for energy generation, chemical synthesis, and hydrogen production, offering a flexible and environmentally advantageous alternative to traditional combustion methods.
The Gasification Process
Feedstock Preparation
The raw material is prepared, which may include drying, grinding, or pelletizing.
Gasification Reactor
The prepared feedstock is fed into a gasifier, where it undergoes partial oxidation at high temperatures (typically 700-1500°C) in the presence of a controlled amount of oxygen or steam.
Syngas Cleanup
The produced syngas is cleaned to remove impurities, such as particulates, sulfur compounds, and tar.
Syngas Utilization
The cleaned syngas can be used for various applications, including power generation, chemical production, and fuel synthesis.
Benefits of Gasification
Gasification provides efficient conversion of low-value feedstocks into valuable energy products, optimizing resource use and enhancing energy output. It significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering emissions of pollutants such as sulfur and nitrogen oxides compared to traditional combustion methods. Additionally, gasification supports diverse applications, including power generation and chemical production, and contributes to sustainable energy solutions by utilizing waste and biomass.:
- Efficient Energy Conversion: Gasification allows for the efficient conversion of low-value feedstocks into high-value energy products.
- Flexibility in Feedstock: Can process a wide range of materials, including coal, biomass, municipal solid waste, and industrial waste.
- Environmental Benefits: Reduces emissions of pollutants, such as sulfur oxides (SOx) and nitrogen oxides (NOx), compared to traditional combustion
Applications of Gasification
- Integrated Gasification Combined Cycle (IGCC)
- Chemical Synthesis
- Hydrogen Production
Syngas is a precursor for producing chemicals, such as methanol, ammonia, and synthetic fuels
Gasification is a key technology for producing hydrogen, an essential component of clean energy systems